Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) was best known for his hierarchy of needs, a theory of psychology based on fulfilling innate human needs in priority order, concluding in self-actualisation. You’ve no doubt used his ideas in determining people’s motivation and drivers for performance.
It’s still utilised in many learning interventions, but is thought of as being dated in relation to today’s technological world with its globalised infrastructure.
One theory that has gained lots of followers is Tony Robbins’ complementary ideas, which he calls our ‘human needs’. Tony states that we consistently work on satisfying those needs at both a conscious and unconscious level of awareness.
Follow Tony Robbins on Twitter
Every single day you are unconsciously striving to meet these “needs” with varying levels of success. Every day, situations occur where these needs can be verified or unconfirmed. And because they are innate ‘needs’ we can utilise these during our training programmes with all of our delegates.
Here are the six needs:
Certainty: assurance you can control what happens to you
Uncertainty/Variety: the need for the unknown, change, new stimuli
Significance: feeling unique, important, special or needed
Connection: a strong feeling of closeness or union with someone or something
Growth: an expansion of capacity, capability or understanding
Contribution: a sense of service and focus on helping, giving to and supporting others
As these are specific needs we all have, it would be appropriate for us to determine how they can be included in our learning and development programmes. Let’s see what could be included at each level:
 1) Certainty
1) Certainty
This is where our comfort zone lies. It gives us a feeling of security and safety. Even if we are going through pain currently (maybe a boring or unchallenging job) we may stick with it because we feel certain we have a degree of security (maybe financially or emotionally).
So how can we fulfil this need in others?
Here are some suggestions:
- Give people a clear path to travel on for their career prospects
- Highlight directions people can take to ensure security in their role
- Build a foundation for people to build their job security
- Allow people to choose what makes them secure in their jobs
- If they are on an L&D programme, make sure they have all the correct logistics for attendance
- Ask them what they require from a programme that will make them confident to learn new ideas
- Identify what delegates in training already know, so they can relate new learnings to existing knowledge
- Increase certainty in what they will experience by being open with information and materials
 2) Uncertainty/Variety
2) Uncertainty/Variety
Being certain gives us security and safety, but can end up in boredom and unfulfillment. We also need to have interesting, challenging and unpredictable events to spice up our lives.
How can we help people to have this need fulfilled?
Here are some suggestions:
- Ask people to take some risks in making projects more stimulating and rewarding
- Introduce different ways of producing materials
- Run the learning with a variety of formats
- Look at job or role-sharing opportunities
- See how different times could be used to start and finish training sessions
- Provide a variety of refreshment options
- Determine different training interventions, using technology and/or games to transfer knowledge
 3) Significance
3) Significance
Feeling unique, different, important or special is one of those needs that act as subliminal drivers for us. We want others to recognise our contribution as this increases our self-esteem and our own self-worth. We can assist in this need in a number of ways:
- Try to personalise each learning experience for the person
- Ask their opinions on items where their knowledge may be greater than others
- Help them to develop their coaching and mentoring skills
- Ask them to share experiences during learning sessions
- Ask them to be part of a team generating case studies for learning sessions
- Build programmes around the specific needs of individuals
- Give individual attention where possible to build their confidence
- Recognise initiatives individuals take and personalise any rewards
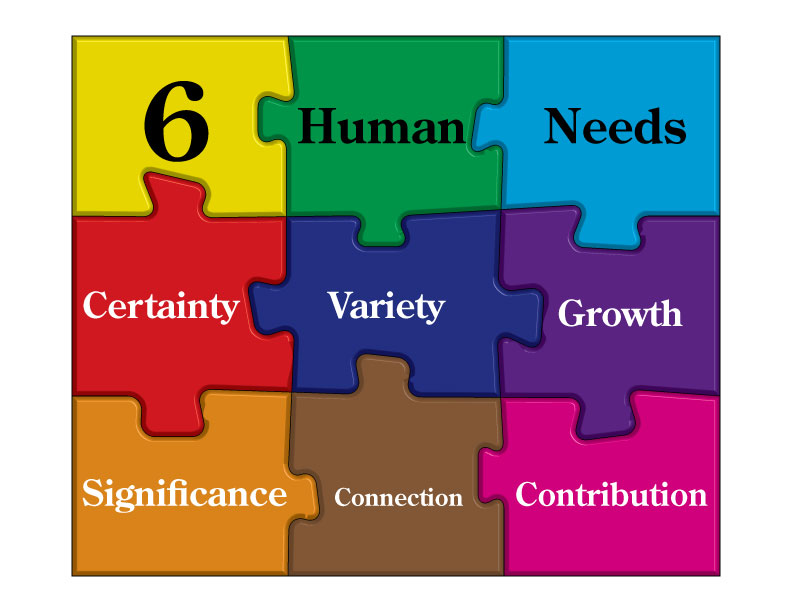
Image from Co-Sulting
 4) Connection
4) Connection
This strong union that a person feels with another person or something will be satisfied by offering chances for people to work in groups or teams and by sharing knowledge between people. To deal with this need, here are some options:
- Create team games that bond group members
- Allow exercises where individuals have to work with others to find answers
- Work with people in groups to find their best mode of working
- Get people to create case studies together
- Identify how learning ideas are linked with already-existing knowledge, so they can be connected and related
- Identify how people’s ideas can be integrated so they synergise with the new ideas discussed
 5) Growth and Development
5) Growth and Development
A universal law is that everything either grows or dies. The subliminal message from that adage is that, unless someone is learning, growing and developing, they are static and suffering from homeostasis. Our role in L&D is to offer those opportunities for people to advance through learning opportunities. Here are some ways:
- Link people’s development with learning chances, both formally and informally
- Personalise learning to a person’s role
- Personalise it to their learning style
- Recognise that people have different learning speeds
- Provide different and varied learning sessions to utilise people’s needs for variety in growing their knowledge
- Build on-line and virtual learning bases for people to deep-dive into their abilities
- Create learning receptacles for people to share information
- Construct individualised and targeted learning programmes for teams and groups, as well as individuals
 6) Contribution
6) Contribution
Tony Robbins last human need is the ability to contribute. This links with our altruistic intentions and satisfies the need to feel we are making some sort of difference.
It forms part of our identity, and builds our esteem by creating solid meaning to our lives. It also links to connecting with others, making a difference and contributing to others’ success.
Here are some suggestions for applying this specific need:
- Look for chances for people to share ideas
- Create reasons for people to build knowledge banks that can be accessed by all
- Show people you appreciate their contribution to activate their need for consistency
- Ask for case studies that would help others to develop their skills
- Identify how people can add to the knowledge base by coaching or mentoring others
- Get people to design quizzes on training programmes to test others’ knowledge
- Design programmes where individuals offer help to others to learn ideas and increase their knowledge
Although Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy helped people to see how we could be motivated as various needs were satisfied, Robbins’ list brings it more up to date within 21st century businesses. His list of six needs can be fulfilled using many ideas in learning and development.
When we develop greater self-awareness, we can consider ways to meet those needs and be more resourceful in the way we help people to achieve them; being able to help others achieve them as well through the above means and more will contribute much to their overall development and engagement in the workplace.

Sean McPheat | 
CEO
The MTD Training Group